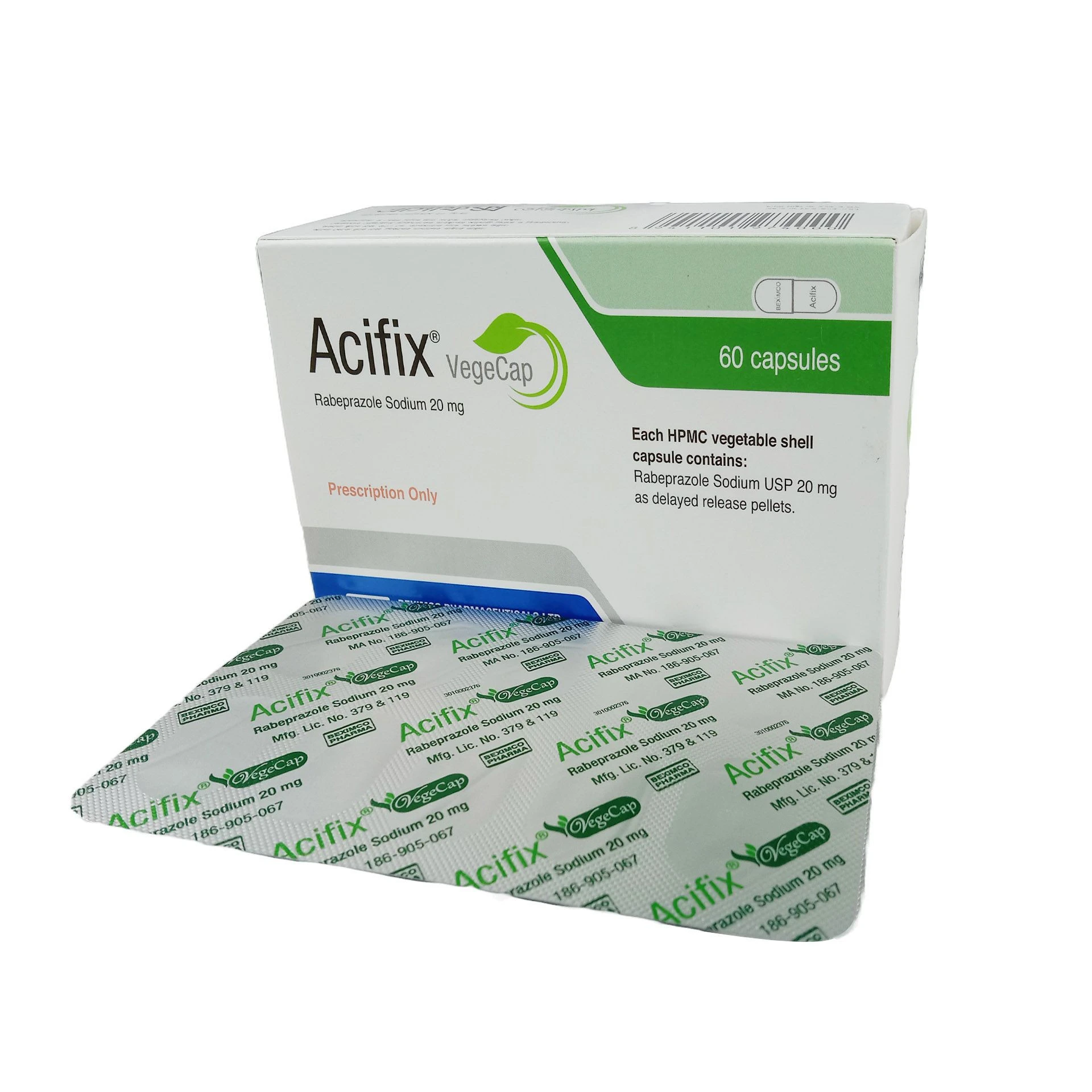
No review given yet!
 Fast Delivery all across the country
Fast Delivery all across the country
 Safe Payment
Safe Payment
 7 Days Return Policy
7 Days Return Policy
 100% Authentic Products
100% Authentic Products
You need to Sign in to view this feature
This address will be removed from this list