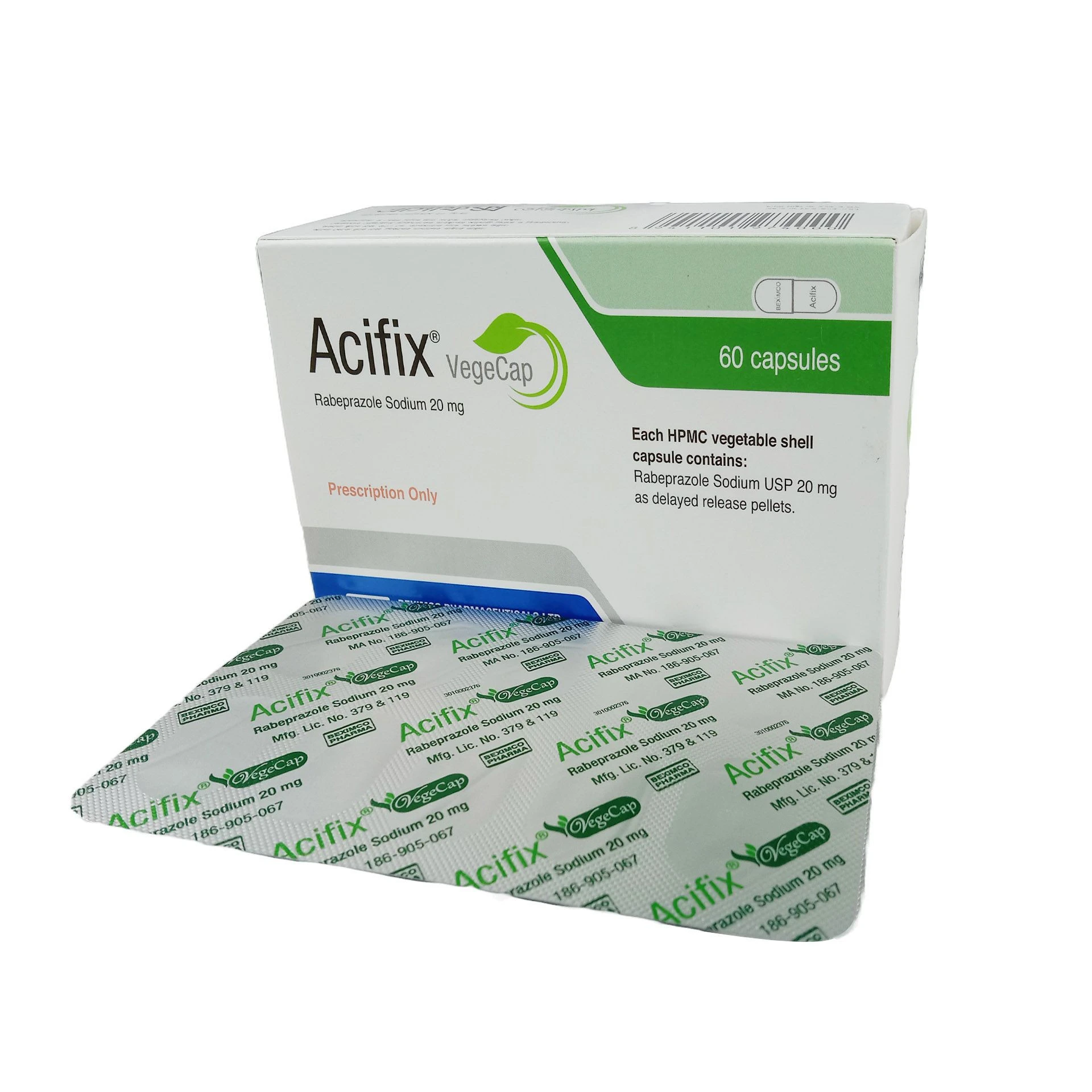
Capsule: Adult dose: The usual dose is 250 mg every 8 hourly. For severe infections or those caused by less susceptible organisms, doses may be doubled with a maximum dosage of 4 g/day. In case of β-hemolytic Streptococcal infections, therapy should be administered for at least 10 days.
Powder for suspension & Pediatric drops: Children: The usual daily dosage for paediatric patients over 1 month is 20 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 8 hours. In serious infections such as otitis media and infections caused by less susceptible organisms, 40 mg/kg/day are recommended, with a maximum dosage of 1 g/day. Safety and effectiveness of Cefaclor for use in infants less than 1 month of age have not been established.
<1 year (9 kg):
- Powder for suspension: ½ tsp three times daily
- Pediatric drops: 0.625 ml three times daily
1-5 years (9 kg-18 kg):
- Powder for suspension: 1 tsp three times daily
- Pediatric drops: 1.25 ml three times daily
Over 5 years:
- Powder for suspension: 2 tsp three times daily
In renal impairment: Cefaclor may be administered in the presence of impaired renal function. Dose adjustments for patients with moderate or sever renal impairment are not usually required.
In patients undergoing haemodialysis: Haemodialysis shortens serum half-life by 25-30%. In patients undergoing haemodialysis, a predialysis loading dose of 250 mg-1 g is recommended. A maintaining dose of 250-500 mg every 6 hourly during interdialytic period may be used.
Geriatric use: Clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.


 Fast Delivery all across the country
Fast Delivery all across the country
 Safe Payment
Safe Payment
 7 Days Return Policy
7 Days Return Policy
 100% Authentic Products
100% Authentic Products