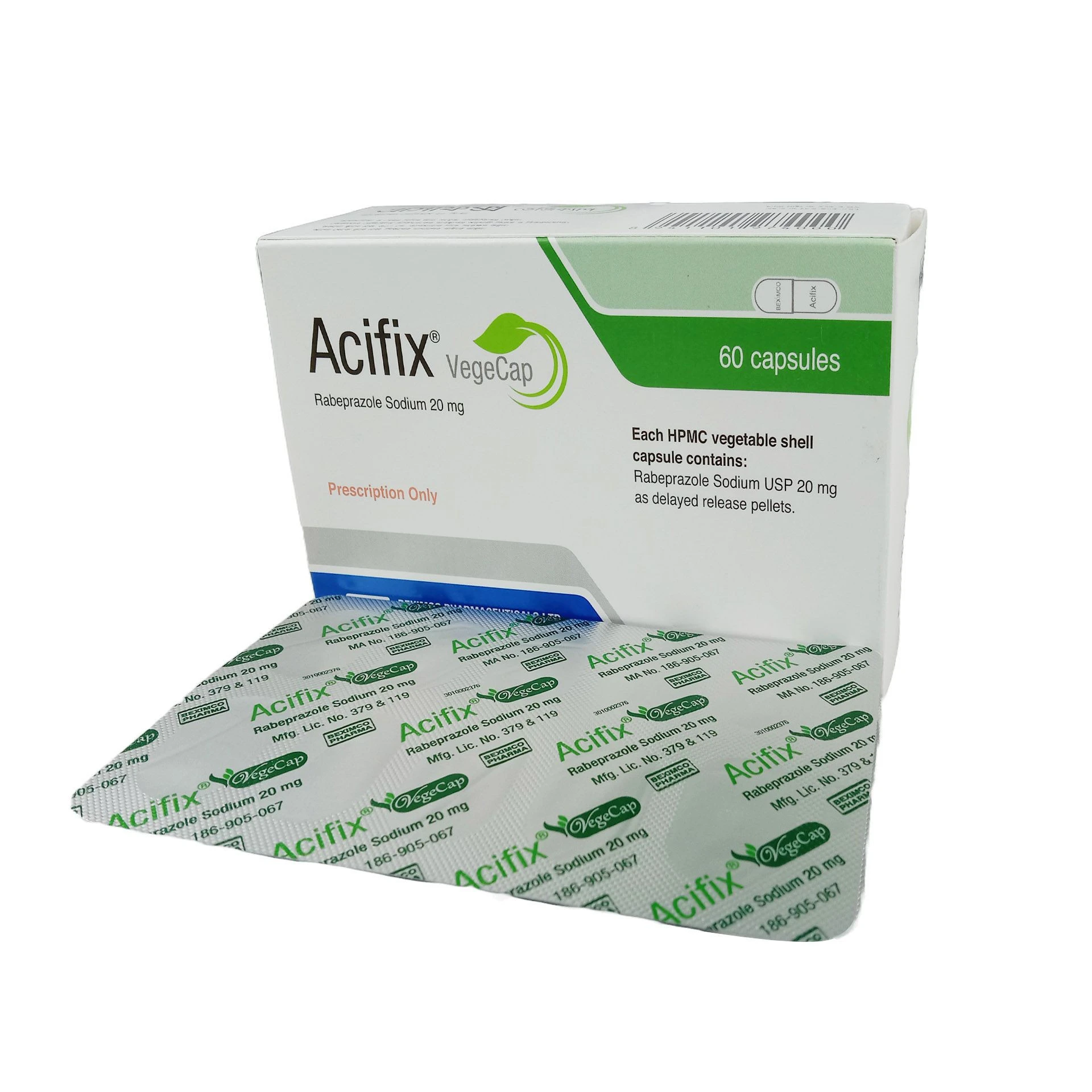
Nebuliser Solution: Use of the nebulizer solution should be subject to close medical supervision during initial dosing. Caution is advocated in the use of anticholinergic agents in patients with narrow-angle glaucoma, or with prostatic hyperplasia or bladder-outflow obstruction or cystic fibrosis. Immediate hypersensitivity reactions have been demonstrated by rare cases of urticaria, angioedema, rash, bronchospasm, oropharyngeal edema and anaphylaxis. There have been isolated reports of ocular complications (i.e. mydriasis, increased intraocular pressure, narrow-angle glaucoma, eye pain) when aerosolized Iprex has come into contact with the eyes during nebulizer therapy.
- Patients must be instructed in the correct administration of the Iprex Nebulizer Solution.
- Care must be taken not to allow the solution or mist to enter the eyes.
- It is recommended that the nebulizer solution is administered via a mouthpiece.
- If a mouthpiece is not available and a nebulizer mask is used, it must fit properly.
Inhaler: Patients should be advised that temporary blurring of vision precipitation or worsening of narrow-angle glaucoma or eye pain may result if the aerosol is sprayed into the eyes. If recommended dosage does not provide relief or symptoms become worse, patients should seek immediate medical attention. While taking
Iprex inhalation aerosol, other inhaled drugs should not be used unless prescribed.
Iprex inhalation aerosol is not indicated for the initial treatment of acute episodes of bronchospasm where rapid response is required. Drugs with faster onset may be preferable as initial therapy in this situation. Immediate hypersensitivity reactions may occur after administration of Iprex, as demonstrated by rare cases of urticaria, angio-oedema, rash, bronchospasm and oropharyngeal oedema.


 Fast Delivery all across the country
Fast Delivery all across the country
 Safe Payment
Safe Payment
 7 Days Return Policy
7 Days Return Policy
 100% Authentic Products
100% Authentic Products